Orchestrate personalized workflows is the strategic capability that turns data and AI into consistent, human centered journeys across customers and employees. In this post I outline pragmatic approaches to design and deliver personalized customer and employee journeys using agentic AI while preserving governance, security, and operational scale. You will find architecture patterns, governance guardrails, rollout playbooks, metrics to track, and a roadmap to move from pilot to production.
This is written for leaders and practitioners who must operationalize personalization across large organizations. You will learn how to orchestrate personalized workflows with predictable outcomes, how to integrate agents into existing systems of record, and how to ensure that governance and observability do not become afterthoughts. The guidance blends technical patterns, organizational practices, and measurable milestones to reduce risk and accelerate impact.
Why enterprises must orchestrate personalized workflows now
Enterprises face rising customer expectations and complex employee needs. To stay competitive, teams must coordinate many systems and decisions so interactions feel tailored and timely. When you orchestrate personalized workflows you connect data, decisions, and actions into a single flow that adapts to context. That is what separates ad hoc personalization from dependable experience automation. Learn more in our post on Troubleshooting Common Failures in AI-Driven Workflows.
Personalization at scale requires solving three hard problems at once. First, you must unify identity and contextual data across channels to create a reliable view of intent. Second, you must define decision logic that maps context to actions and responses. Third, you need operational controls and observability so that the system can be tested, audited, and improved over time.
When organizations learn to orchestrate personalized workflows they unlock higher conversion rates, faster resolution times, and stronger employee productivity. The gains compound when workflows can be composed, reused, and governed. The rest of this article describes patterns and practices to reach those outcomes without sacrificing control.
Core architectural patterns to orchestrate personalized workflows
At the core of any scalable personalization strategy is an orchestration layer that coordinates inputs, decisioning, and execution. This layer is distinct from the UI, the data stores, and the model endpoints. It is the conductor that tells systems and agents what to do next. When you architect to orchestrate personalized workflows focus on separation of concerns and clear interfaces. Learn more in our post on Sustainability and Efficiency: Environmental Benefits of Automated Workflows.
Start with a lightweight orchestration runtime that supports event driven triggers, long running flows, and state management. The runtime should allow declarative flow definitions, support integrations to internal and third party systems, and provide hooks for human in the loop interactions. This runtime is where agents, business rules, and third party services are assembled to produce a personalized outcome.
Design flows to be composable. Break journeys into reusable building blocks such as identity resolution, intent classification, offer selection, and fulfillment. Each block should present a well defined contract so it can be replaced or improved independently. Composability helps teams rapidly assemble new personalized journeys without rebuilding core capabilities.
Data and identity layer
Reliable personalization depends on a consistent identity and context model. Build a canonical identity service that unifies identifiers, consent signals, preferences, and permissions. Ensure it can answer queries at low latency and serve both online and batch workflows. Privacy and regulatory constraints must be enforced centrally so that any time you orchestrate personalized workflows the system respects those guardrails.
Invest in a consistent context store that aggregates signals such as recent behavior, transaction history, and agent interactions. The context store should maintain historical state for analysis and summary state for real time decisioning. Keep data models simple and versioned so personalization logic remains comprehensible and auditable.
Decisioning and agent layer
Decisioning is where business intent is translated into actions. Use hybrid approaches that combine deterministic rules, learned policies, and agentic AI. Agentic AI can improve relevance by synthesizing context, predicting next best actions, and managing multi step tasks, but always place a decisioning layer between agents and execution endpoints to validate outputs.
Implement typed outputs for agents so that downstream systems receive structured information. When you orchestrate personalized workflows enforce schema contracts for agent responses. This reduces friction and makes it easier to introduce new agent capabilities without breaking integrations.
Execution and integration
Execution components perform tasks such as sending messages, creating tickets, updating records, and invoking services. Use connectors or integration adapters that abstract the specifics of each system. This enables the orchestration runtime to call a consistent API for common actions. By doing so you can swap integrations or add new channels without changing the flow logic.
Design for idempotency and eventual consistency. Enterprise systems often require retries and compensating actions. When you orchestrate personalized workflows ensure each step is retriable and that side effects are auditable so you can diagnose issues without manual reconciliation.
Governance, safety, and compliance for agentic personalization
Bringing agentic AI into production requires explicit governance. Governance is not only a policy document. It is the tooling and processes that ensure behavior is consistent with organizational values, regulatory requirements, and customer expectations. A governance framework helps teams decide when to automate, when to include humans, and how to handle errors. Learn more in our post on Security and Compliance for Agentic AI Automations.
Start by defining policy categories such as consent, data retention, acceptable use, and escalation thresholds. Map policies to enforcement mechanisms in the orchestration runtime. For example enforce consent by failing flows that require data without proper flags. This helps ensure that every time you orchestrate personalized workflows there is a systemic check that prevents unauthorized actions.
Create a model risk management practice for agents. This includes versioning models, tracking training data provenance, and running regular performance tests. Use synthetic tests and production shadow modes to surface undesired outputs before releasing changes to live traffic. When you orchestrate personalized workflows maintain an audit trail for every decision the system makes so you can explain outcomes to regulators and stakeholders.
Human oversight and escalation
Even the best automated flows will encounter edge cases that require human judgment. Design clear human in the loop patterns with contextual handoff screens and explanatory summaries. Provide case owners with the provenance of decisions, the confidence scores, and the recent interaction history so they can act quickly.
Establish escalation rules for high risk scenarios. When you orchestrate personalized workflows ensure the runtime can pause or route flows to designated reviewers based on rules or anomaly detection. This keeps accountability intact while scaling automation.
Security and least privilege
Embed security practices early. Integrate single sign on, fine grained permissions, and service level authentication between orchestration components and downstream systems. Log all access and changes so you can trace operations. When you orchestrate personalized workflows follow least privilege principles for connectors and agents to reduce the impact of compromised credentials.
Operationalizing agentic AI across customer and employee journeys
Agentic AI is effective when it is a component of a broader orchestration strategy rather than a point solution. Agents can handle tasks such as summarizing interactions, drafting responses, or executing multi step processes. But to operate at enterprise scale you must manage agents like any other service with SLAs, monitoring, and deployment practices.
Create agent categories with clear responsibilities. For example define advisory agents that suggest actions, executor agents that perform sanctioned tasks, and escalation agents that detect and route uncertain cases to humans. This separation clarifies risk and simplifies governance when you orchestrate personalized workflows involving agents.
Develop a deployment pipeline for agents that mirrors software engineering practices. Include unit tests, integration tests, and canary releases. Use production shadowing to compare agent outputs with existing human or rule based decisions before fully switching traffic. This reduces surprises and builds confidence among stakeholders.
Feedback loops and continuous learning
Design explicit feedback loops so agents learn from outcomes. Capture signals such as acceptance, edits, rework, and downstream conversions. Feed these signals into retraining pipelines and business rule updates. When you orchestrate personalized workflows ensure feedback is collected at the point of decision and aggregated for model governance.
Feedback also includes qualitative signals from human reviewers. Use periodic review panels to sample agent decisions, document failure modes, and prioritize fixes. Combining automated metrics with human insight accelerates continuous improvement.
Scaling and cost control
Running agents and orchestration at scale requires cost discipline. Use caching, batching, and efficient model routing to manage compute usage. Prefer smaller specialized models for routine tasks and reserve larger models for low frequency, high complexity cases. Architect the orchestration runtime to choose the right resource for each step so you can control cost while still delivering high quality personalization.
Monitor latency and throughput to ensure the system meets business needs. When you orchestrate personalized workflows set performance budgets and alerting so teams can react quickly to degradation or spiky demand.
Implementation roadmap to orchestrate personalized workflows
Moving from concept to production is a staged process. Use a phased roadmap with clear acceptance criteria for each stage. A common approach includes discovery, prototype, pilot, and scale phases. Each phase should validate both technical feasibility and business value when you orchestrate personalized workflows.
- Discovery: Map high value journeys, identify data sources, and prioritize use cases. Engage stakeholders from product, legal, security, and operations. Document required integrations and compliance constraints.
- Prototype: Build a narrow proof of concept that demonstrates the orchestration runtime, a sample agent, and a basic identity context. Validate that the flow can deliver measurable improvements in a controlled environment.
- Pilot: Expand to a small user population. Introduce governance checks, logging, and human oversight. Run A B tests or holdout experiments to quantify impact. Iterate based on feedback and operational metrics.
- Scale: Harden integrations, enable multi tenancy where applicable, and automate deployment pipelines. Add monitoring dashboards, alerting, and cost controls. Document playbooks for incidents and change management.
Throughout the roadmap keep change small and reversible. Feature flags and progressive exposure reduce blast radius and support rapid rollback if a change has unintended consequences. When you orchestrate personalized workflows ensure each incremental step has rollback controls and observable success criteria.
Use case patterns to prioritize
Prioritize workflows that offer high value and low complexity to test the orchestration approach. Good starter use cases include personalized onboarding flows, issue resolution routing, renewal and retention outreach, and internal employee service automation. These workflows typically have clear success metrics and frequent volume, which makes it easier to measure improvements.
Once you prove value on foundational flows, expand to more complex cross channel orchestrations that involve third party services and long running interactions. Maintain a catalog of reusable orchestration blocks so new teams can adopt the pattern quickly and safely. This catalog is a core asset when you orchestrate personalized workflows across multiple business units.
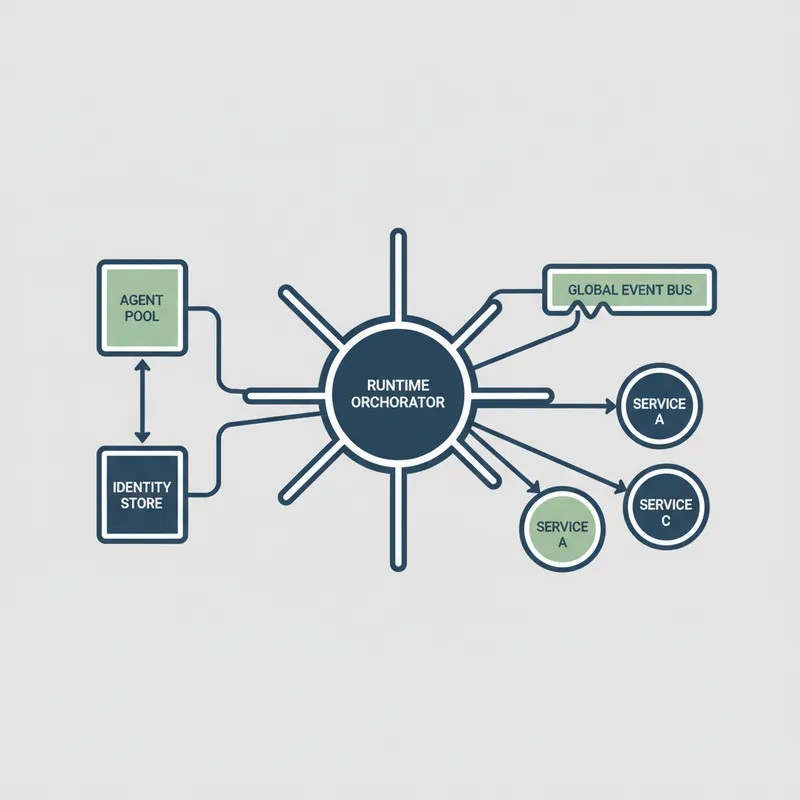
Best practices for testing, observability, and resilience
Testing and observability are essential to trust. Implement layered testing that includes unit tests for flow logic, integration tests for connectors, and end to end tests for user journeys. Use synthetic monitoring to exercise critical paths and detect regressions before users are impacted. When you orchestrate personalized workflows build a test harness that can replay production events with scrubbed data to validate changes.
Observability should capture telemetry at both the orchestration level and the agent level. Track metrics such as decision latency, success rates, escalation percentage, and model confidence distributions. Correlate these metrics with business outcomes like conversion rates and time to resolution. Dashboards and alerts help teams identify trends and prioritize improvements.
Resilience strategies must include retries, circuit breakers, and graceful degradation. Define fallback behaviors for when an agent or external service is unavailable. For example route to a limited feature path or queue the request for later processing. When you orchestrate personalized workflows ensure that failure modes are visible and that recovery is automated where possible.
Canarying and progressive delivery
Roll out changes gradually using canaries and feature flags. This allows teams to validate new decision logic or agent models with a small subset of traffic. Monitor both technical metrics and business KPIs during the canary window. If performance or behavior diverges, use the feature flag to revert instantly.
Progressive delivery is particularly important for personalization since small changes can have outsized effects on user experience. When you orchestrate personalized workflows design experiments that capture both immediate outcomes and downstream impacts across multiple touchpoints.
Auditability and explainability
Provide structured explanations for automated decisions. Store decision traces that include input context, agent outputs, rule evaluations, and final action. These traces support debugging, compliance audits, and appeals from customers or employees. Explainability is a competitive advantage because it builds trust when the system behaves transparently.
Measuring impact and continuous optimization
Define success metrics early. For customer journeys common metrics include conversion rate, average handling time, net promoter score, and retention. For employee journeys include time to resolution, case backlog, and employee satisfaction. Link these metrics to financial outcomes to justify investment and prioritize roadmap items when you orchestrate personalized workflows.
Use experimentation to validate assumptions. A B testing is critical for personalization because it prevents false positives from uncontrolled rollouts. Structure experiments to measure both immediate and delayed effects. For example a personalized offer may increase conversions but reduce margin; track both to make informed trade offs.
Invest in attribution models that can attribute outcomes to orchestration decisions. Multi touch attribution helps you understand which parts of a personalized workflow drive value. When you orchestrate personalized workflows use these insights to prune low value paths and invest in high impact enhancements.
Optimization loops
Optimization is iterative. Use a four step loop: observe, hypothesize, experiment, and learn. Observe baseline metrics and identify friction points. Hypothesize targeted changes such as adjusting thresholds, rewriting prompts, or altering routing rules. Experiment using controlled rollouts. Learn from results and incorporate winning changes into the mainline flows.
Automation can accelerate optimization. Implement systems that detect degraded performance and propose candidate changes. Human review remains essential, but automation can surface opportunities that manual analysis might miss. When you orchestrate personalized workflows combine automated signals with human judgment to scale improvements safely.
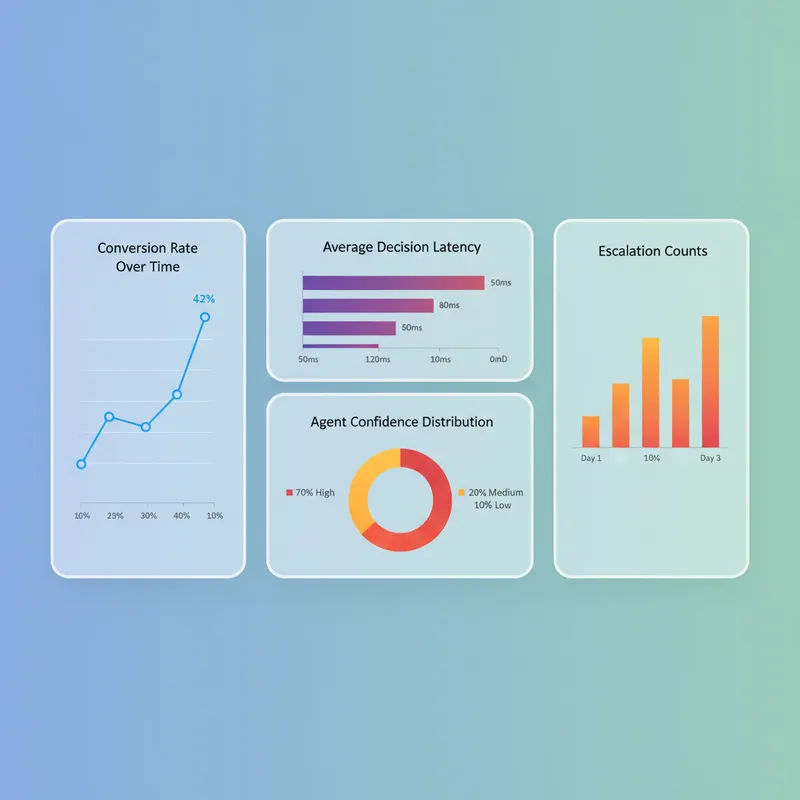
Organizational practices that support scale
Technology alone will not deliver personalization at scale. Organizational alignment, clear ownership, and cross functional collaboration are required. Establish a central team for the orchestration platform that provides shared primitives, governance, and technical support. This center of excellence can help business teams adopt the platform and ensure consistency when you orchestrate personalized workflows.
Define roles and responsibilities across teams. Platform engineers manage the runtime and integrations. Data engineers curate context stores. Model owners handle agent training and evaluation. Product teams design journey definitions and success metrics. Legal and compliance review policies. When everyone understands their role the organization can move faster and reduce duplication of effort.
Invest in developer experience. Provide SDKs, templates, and a library of flow blocks so teams can assemble personalized journeys without deep platform knowledge. Good documentation and examples accelerate adoption. When you orchestrate personalized workflows make it easy for product teams to experiment safely.
Change management and training
Introduce change incrementally and provide targeted training for product owners and reviewers. Use workshops and playbooks to teach teams how to map business intent to flow blocks and how to interpret observability dashboards. Equip reviewers with the tools to evaluate agent outputs fairly and consistently.
Recognize that governance can be perceived as friction. Frame governance as an enabler that reduces risk and increases confidence. When you orchestrate personalized workflows build empathy into the rollout plan and collect feedback to improve processes.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
Many organizations attempt personalization with high expectations but stumble on execution details. Common pitfalls include insufficient identity resolution, weak testing, lack of rollback mechanisms, and inadequate governance. The antidote is disciplined engineering practices and clear policies.
Avoid brittle integrations by building abstraction layers and testing connectors thoroughly. Do not let model outputs directly trigger irreversible actions without validation. Use approval gates and human review for high risk operations. When you orchestrate personalized workflows ensure there are manual overrides and clear incident procedures.
Watch for signal sprawl. Too many personalization features can overwhelm users and staff. Consolidate personalization logic into centralized decision services so you can reason about trade offs across journeys. Periodically audit personalization rules and agent behaviors to remove redundancy and conflicts.
Conclusion
To orchestrate personalized workflows successfully at enterprise scale you must combine architectural discipline, rigorous governance, and organizational alignment. Personalization is most effective when it is treated as a composable service that can be reused across customer and employee journeys. The orchestration runtime becomes the single place where identity, decisioning, agents, and execution converge to create consistent, auditable experiences.
Start with a clear value driven roadmap that prioritizes high impact, low complexity flows. Build a canonical identity and context layer, adopt a composable flow architecture, and introduce a decisioning layer that validates agent outputs. Governance is not optional. It is a core ingredient that ensures trust and regulatory compliance when you orchestrate personalized workflows. Implement model risk practices, human oversight, and extensive auditing to maintain accountability as automation grows.
Operational excellence matters. Invest in testing, canarying, observability, and cost controls to avoid surprises in production. Use progressive delivery and feedback loops so agents and flows can improve iteratively. Organize teams with a central platform that provides primitives and guidance while empowering product teams to innovate safely. Training and change management reduce friction and accelerate adoption.
Finally measure what matters. Tie personalization metrics to business outcomes and run controlled experiments to validate improvements. Attribution and multi touch analysis will reveal which orchestration components deliver the most value. When you orchestrate personalized workflows at scale you create repeatable patterns that amplify impact across the enterprise and deliver measurable benefits to customers and employees.
Orchestration is a long term investment. By focusing on modular architecture, strong governance, and operational rigor you can harness agentic AI to deliver personalized journeys that are reliable, explainable, and scalable. Start small, learn fast, and expand with the confidence that your orchestration foundation can support growth and new capabilities for years to come.